Which Type of Bond Joins Together Two Monosaccharides
Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction a condensation reaction. Monosaccharides are joined together by covalent bonds called glycosidic bonds.

Reading Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Biology I
Two monosaccharide molecules may chemically bond to form a disaccharide.
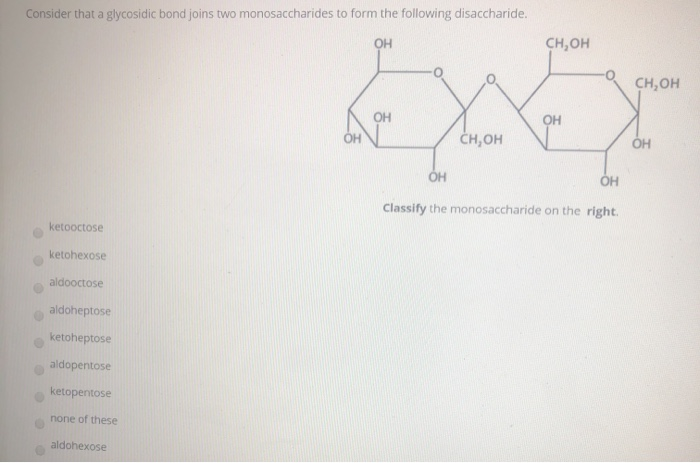
. Monosaccharides such as glucose can be linked together in condensation reactions. This is a strong bond that involves the sharing of electrons. A peptide bond joins two amino acids together to form polypeptides.
These molecules bond together in a specific type of chemical reaction. Glycosidic bonds are the covalent bonds that link the two monosaccharides molecules in a carbohydrate. Three common examples are sucrose lactose and maltose.
First two monosaccharides are brought together such that two hydroxyl groups are close to each other. The two monosaccharides are bonded via a dehydration reaction also called a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis that leads to the loss of a molecule of water and formation of a glycosidic bond. The reaction that links two.
The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a monosaccharide reacts with the OH hydroxyl group of a monosaccharide with the elimination of a H2O molecule ie. Sugars may also become linked to molecules by N-glycosidic bonds and other types of glycosidic bonds. A glycosidic bond is formed via a condensation reaction which is also called dehydration synthesis.
Molecules composed of two monosaccharides are called disaccharides. Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides join together by the dehydration synthesis reaction resulting in a glycosidic bond between the two monosaccharide molecules. Complex carbohydrates are made of one or two saccharides.
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction a water molecule is eliminated leaving a. Glycosidic bonds form between hydroxyl groups of the two saccharide molecules. When a molecule of glucose bonds with another molecule of glucose the disaccharide that is formed is called maltose.
The glycosidic bond is a covalent bond. The quaternary structure multiple polypeptides that come together to form a protein. A glycosidic bond is the result of a condensation reaction which means that one water molecule is produced during the formation of a glycosidic bond.
The type of bond that joins monosaccharides and is easily digested by enzymes in the human intestine is a. The tertiary structure an overall shape of a polypeptide caused by the R group in the amino acids. 2 of 8 1062016 422 PM.
A glycosidic bond is left between the two monosaccharides. A disaccharide forms when two monosaccharides bond together. Which of the following types of bonds joins monosaccharides together to form a polysaccharide.
- glycosidic bonds - peptide bonds - phosphodiester bonds - hydrogen bonds. What bond holds alpha glucose and fructose together. For example sucrose table sugar is formed from one molecule of glucose and one of fructose as shown below.
What type of glycosidic bond is linking these monosaccharides together. Triose oligosaccharide hexose pentose Chapter 05 Reading Quizzes. The bond that joins monosaccharides to form di or polysaccharides is known as glycosidic bond.
We can think about dehydration as the loss of a water molecule. The name given to the covalent bond between the two monosaccharides is a glycosidic bond. The second a helix.
Part A The bond that joins two monosaccharides into a disaccharide is a n _____. They are held together by a covalent bond. The reaction produces water as a side product.
The most common glycosidic bonds connecting monosaccharide units are O-glycosidic bonds in which the oxygen from a hydroxyl group becomes linked to the carbonyl carbon. Dehydration to form a. Complex carbohydrates only contain long chains of glucose molecules joined together.
What type of bond joins two monosaccharides. Sucrose table sugar is the most common disaccharide which is composed of the monomers glucose and fructose. Two monosaccharides are joined to form a disaccharide by a glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage.
The primary structure a chain of amino acids. See Section 52 page 110. What is the reaction that links two monosaccharides together.
Like monosaccharides disaccharides are soluble in water. What bond joins monosaccharides.
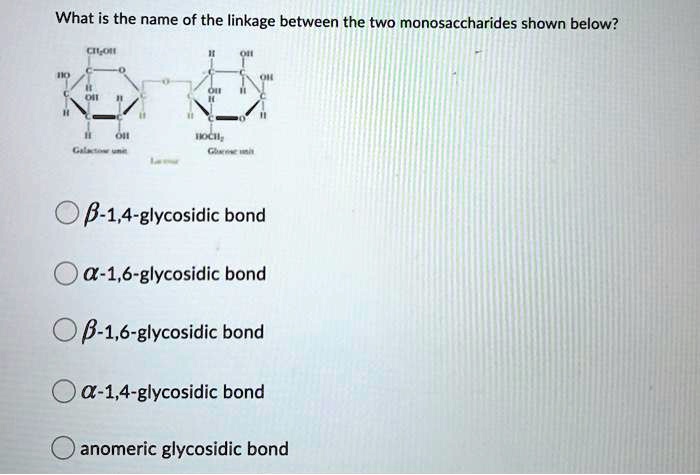
Solved What Is The Name Of The Linkage Between The Two Monosaccharides Shown Below B 1 4 Glycosidic Bond A 1 6 Glycosidic Bond B 1 6 Glycosidic Bond A 1 4 Glycosidic Bond Anomeric Glycosidic Bond
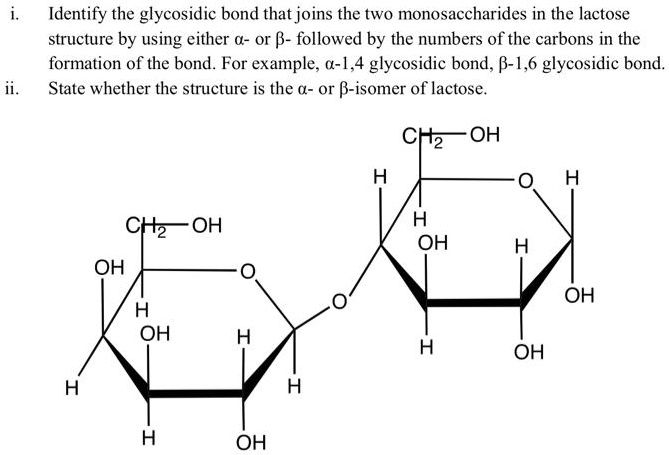
Solved Identify The Glycosidic Bond That Joins The Two Monosaccharides In The Lactose Structure By Using Either G Or B Followed By The Numbers Of The Carbons In The Formation Of The Bond
Comments
Post a Comment